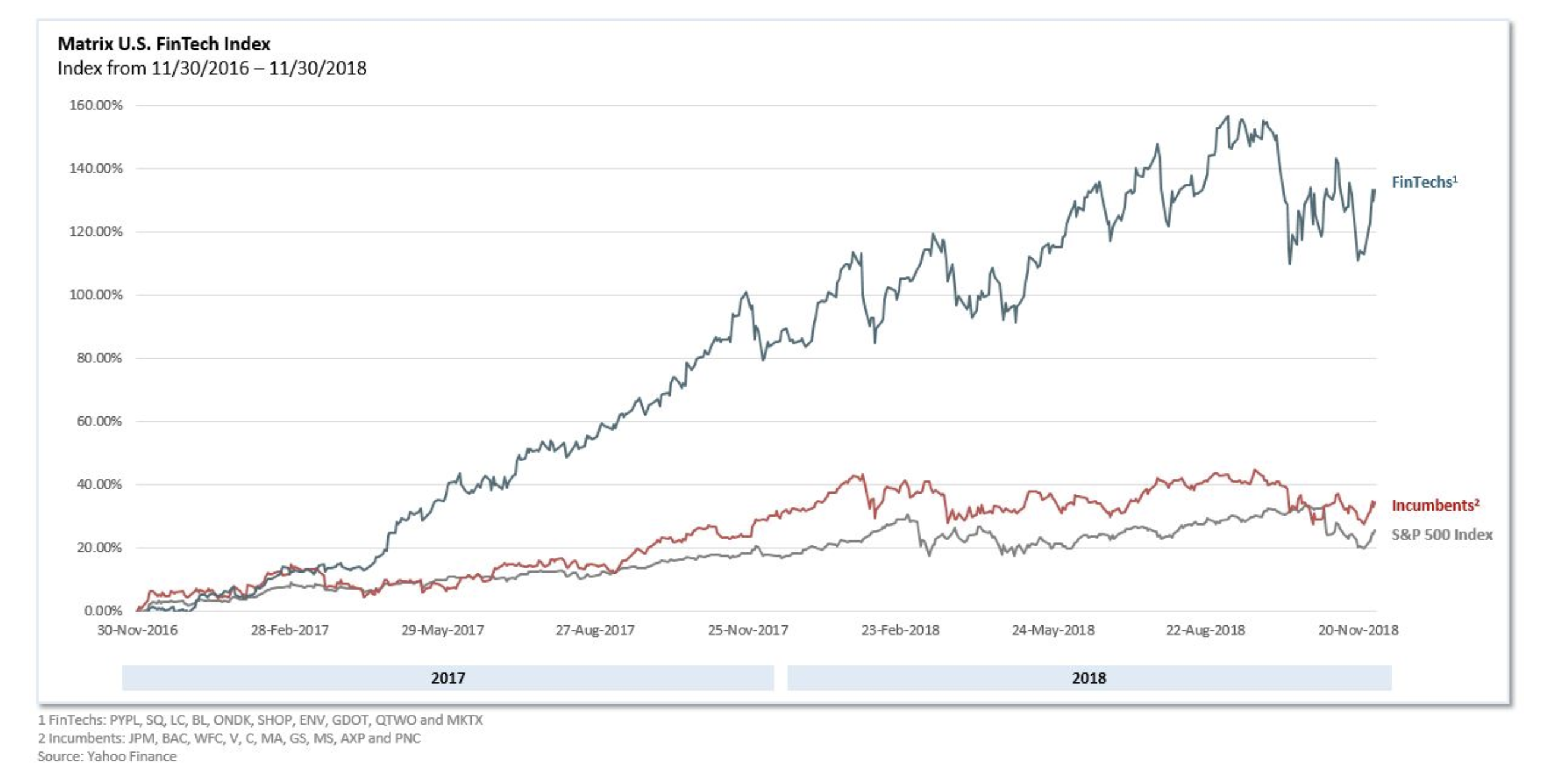
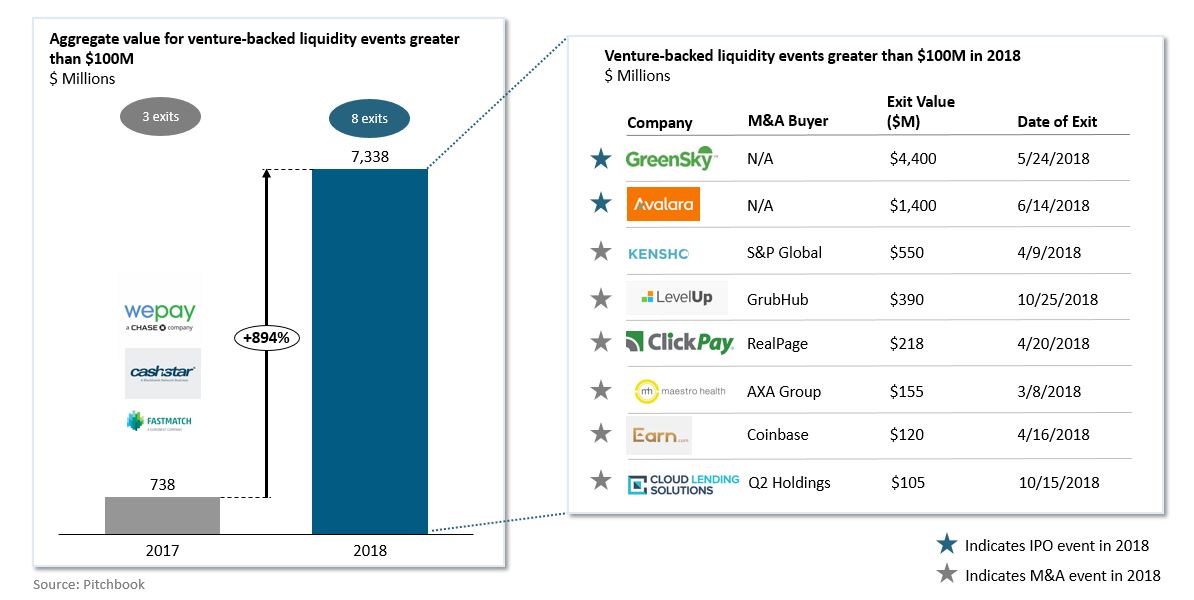
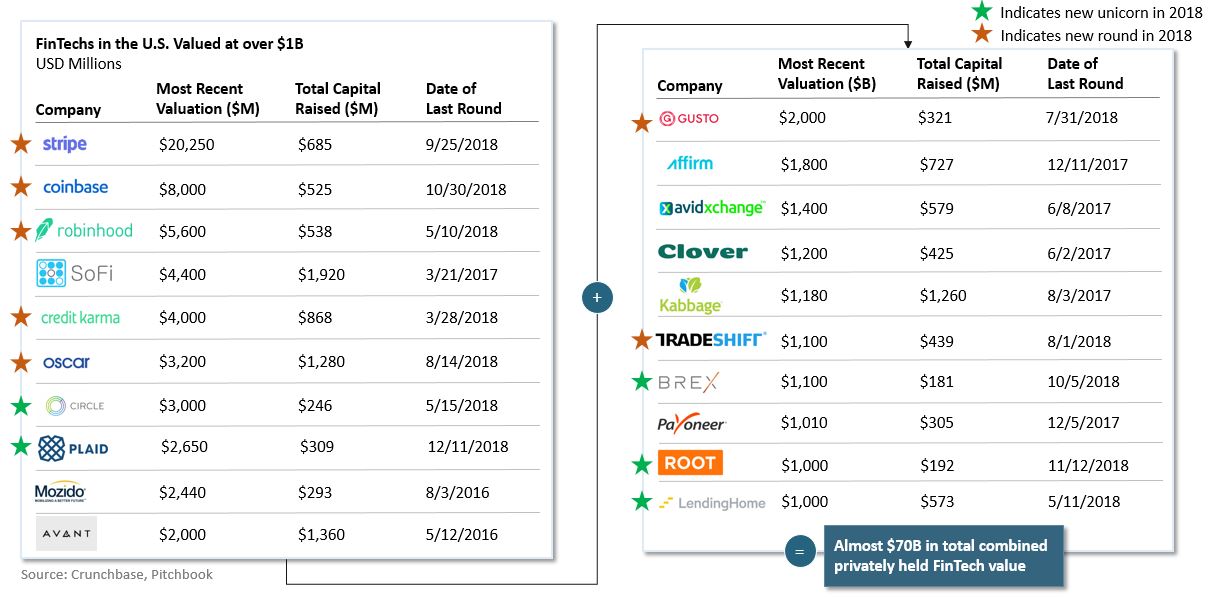
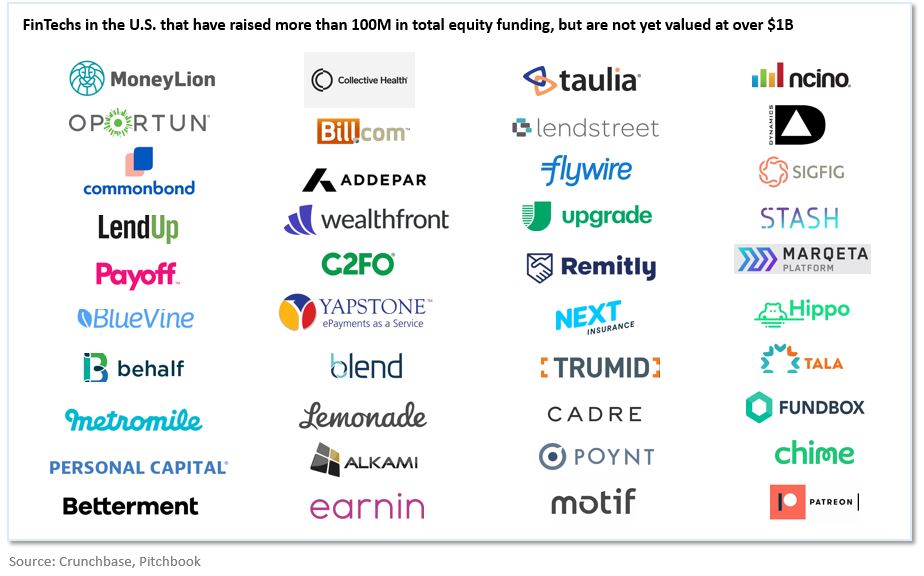
Are rightsholders ready for public domain day?
On January 1, 2019, the New Year will ring in untold numbers of additions to the public domain in the U.S., including hundreds and maybe thousands of works with at least a small public reputation. This, of course, is due to the expiration of the terms of their copyrights, some of which have been extended multiple times since the 1960s.
This is a good thing from many perspectives, including that of authors, publishers, museum curators, teachers, old-book readers and music and film buffs. It possibly may be a slightly bad thing for a few people — primarily certain estates representing long-dead authors and other creators.
What’s a “term” in the context of copyright?
The duration, or term, of U.S. copyright is set by Congress, and has gradually crept up over time from the original 14 years (plus 14 more if the author was still alive and renewed the copyright) — in Thomas Jefferson’s time — to a whopping “life of the author plus 70 years,” as set by the 1998 “Copyright Term Extension Act” (CTEA, which extended it from life plus 50).
For works first published between 1909 and 1978, the maximum term was finally set by Congress at 95 years (assuming the author complied with a whole lot of rules, alluded to below). And for post-1978 works, in instances where the author/creator is not a human being (such as a business commissioning a “work made for hire” under rules developed in the case-law) or the work was published under a pseudonym for an unknown person, the term can be as long as 120 years! The copyright in a work, duly registered at the time that registration was required (pre-1978), may never have been renewed, and so its protection may have quietly lapsed some time ago; for many more obscure works, it’s hard to know.
Fun fact: This Copyright Term Extension Act is also known as the Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act. Congress named it in memory of the composer of “I’ve Got You, Babe,” who, as a member of Congress from Southern California, was among the authors of the bill; he unfortunately happened to die while it was being worked on in committee. Prior to 1978, the term of U.S. copyrights was determined by fixed terms of years, subject to publication, registration and notice requirements. Here are more details on that.
How do works pass into the public domain?
Currently, works pass into the public domain according to a complex schedule, combining (sometimes awkwardly) the rules of various laws implemented over the past century.
Bear in mind, however, that many works have passed (or “fallen” or “lapsed,” as the older phrases had it) into the public domain in the U.S. for reasons other than term expiry, even during the 20 years of the CTEA extension. According to the law in effect prior to 1978, if the work was published but never registered in the U.S. Copyright Office, it did not receive protection under copyright law; a work might also not be protected by U.S. copyright law if it lacked proper notice — the © symbol and the proper wording — or if the work’s registration was not renewed after its first 28-year term expired. Or if, as a work of the federal government, it never enjoyed copyright protection in the first place.
Qui Bono? (get it?)
As it turns out, it is not just re-publishers of “classic” texts, such as Dover Thrift Editions, which benefit when new works become available. Textbook and educational publishers frequently re-use old short stories and essays in larger collections, and a work of marginal utility might become more attractive as a potential addition to these collections once the cost of clearing the rights is reduced.
For example, a few years ago a 1922 story by F. Scott Fitzgerald, “The Curious Case of Benjamin Button,” (whose U.S. copyright had lapsed) was adapted into a feature film. To me, the lesson to be gleaned is that many works of the early 20th century still appear to bear some cultural cachet (or at least continuing value to society) — such that more no-cost access to these works (by their passing from copyright protection to the public domain) should have the overall effect of helping them find new audiences.
Note: Bear in mind, all of these examples are simply illustrative — without a full and careful copyright search, it is difficult to be certain of the copyright status of almost any work. On that, more below.
New works coming into the U.S. public domain also will have the effect of giving researchers new texts to run Text and Data Mining (TDM) algorithms across. It also may add to the richness of film and cultural studies.
Mark Twain proves this isn’t so easy
Unfortunately, determining when a work has in fact “fallen” into the public domain due to the term of its copyright having expired is not always as simple as one might hope.
For example, one might think that everything ever laid down by the pen of Mark Twain (S.L. Clemens, d. 1910) would be in the public domain by now. But, since he left a treasure trove of unpublished works, their copyright protection has extended for many years after his death, because, under pre-1978 law, those works’ copyright protection would not start until the works were published. The distinction between published and unpublished works has been discarded under post-1978 law, but won’t be fully effective for another 30 years. So, some items in the microfilm edition of Twain’s letters and manuscripts (their first publication) are still considered to be under copyright. He’s also enjoyed considerable success recently with the full and final publication of his autobiography.
Twain, a student of intellectual property, steadfastly argued for a perpetual copyright, but he came to realize that this was not permitted under the copyright clause of the U.S. Constitution, which refers to “securing [protection] for limited times.” But, in an age when copyright only protected works for which registrations had been obtained, he did point out that most books wouldn’t be affected by a longer term at all — for the vast bulk of them had no commercial life remaining to them a very few years after their initial publication:
One author per year produces a book which can outlive the forty-two-year limit; that’s all. This nation can’t produce two authors a year that can do it; the thing is demonstrably impossible. All that the limited copyright can do is to take the bread out of the mouths of the children of that one author per year.
I made an estimate some years ago, when I appeared before a committee of the House of Lords, that we had published in this country since the Declaration of Independence 220,000 books. They have all gone. They had all perished before they were ten years old. It is only one book in 1000 that can outlive the forty-two-year limit. Therefore, why put a limit at all? You might as well limit the family to twenty-two children.
– S.L. Clemens, in testimony to Congress, concerning proposed copyright legislation (1906)
“Forever minus a day,” another idea which has been occasionally bruited about (particularly by Congressman Bono and his widow, who was later elected seven times in her own right to Congress), would not constitute much of an effective limit, and so would, I believe, violate the Constitutional limitation; 95 years (an estimated average of the “Life plus 70” term) seems closer to a natural lifespan for a copyright — to me at least. If you and your heirs somehow can’t get the commercial value out of your work before nearly a century is out, I think there’s a takeaway lesson there.
On the other hand…
… some works do have cultural lifespans exceeding the term of copyright. The estates of certain literary, film and musical creators may stand to lose when the copyright in some of the works in their respective repertories lose copyright protection due to the lapse of their terms. For some examples of works entering the public domain on January 1, 2019, that may still have financial value to the author/creator’s heirs: Hemingway’s “Three Stories and 10 Poems” was first published in 1923; it was also the year of release for “Safety Last!” a silent film from Hal Roach Studios, starring Harold Lloyd, which many people remember. The same year saw the first publication (of the sheet music) for “Who’s Sorry Now?” which was a hit recording for Connie Francis in 1958.
But, on balance, “Nothing gold can stay,” as Robert Frost observed in a poem slated — I’m pretty sure — to enter the public domain on January 1st.* The reading, listening, and viewing public should expect to be the main beneficiary of these works entering the public domain. Indeed, 95 years is a good run for the commercial exploitation of a work. Now it’s everybody else’s turn to benefit.
*If it hasn’t already. Copyright searches, on the detail level, can be quite difficult and time-consuming. See: https://www.copyright.gov/rrc/. For any proposed commercial republication, it is certainly the course of wisdom to consult with an attorney and have a full copyright search done.